Architecture
Here is the asynchronous runtime's architecture:
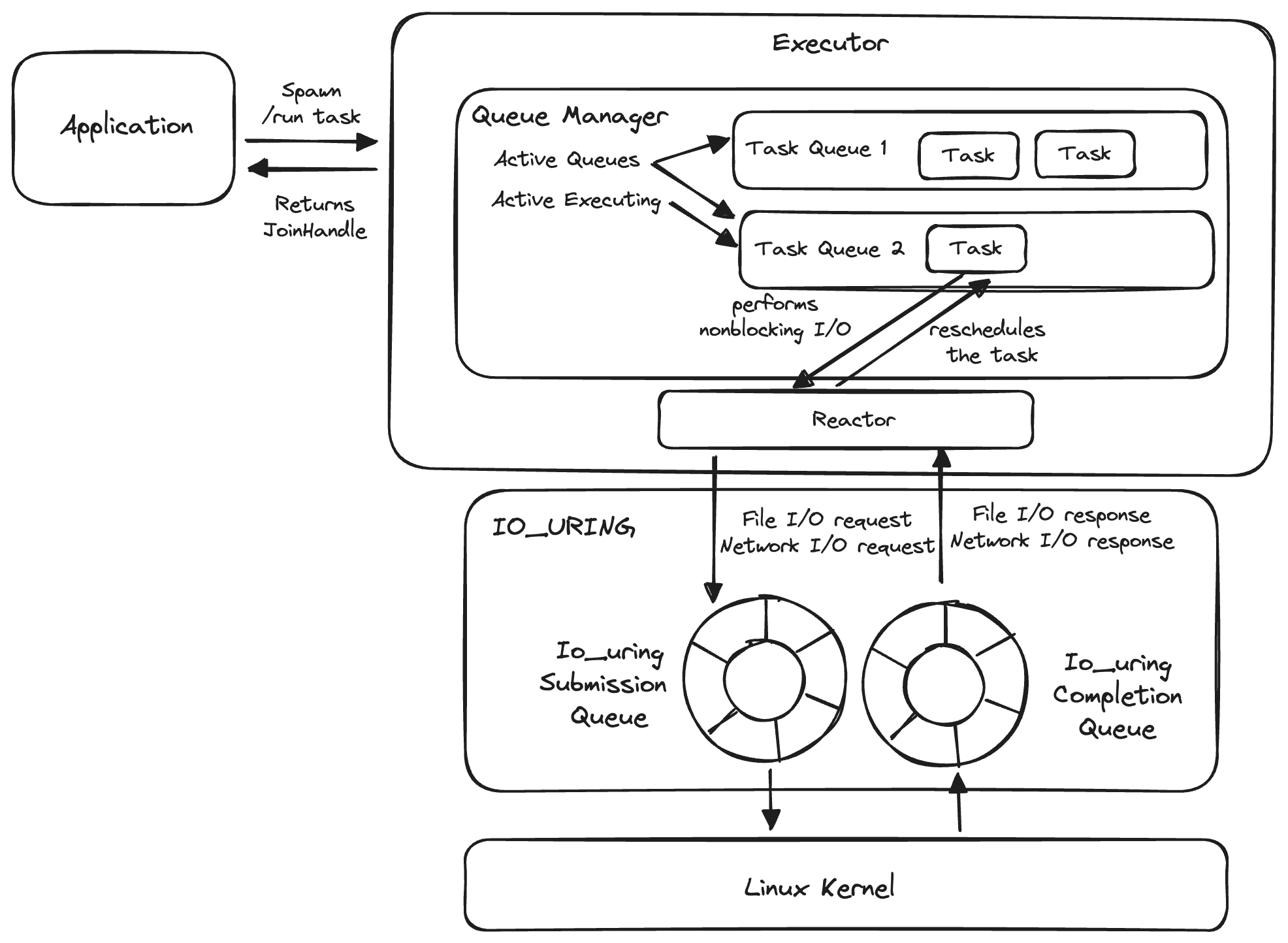
When the programmer spawns a future onto the executor, a task is created and a JoinHandle is returned to the user.
The user can use the JoinHandle to consume the output of the completed task or cancel the task.
The spawned task is placed onto one of the task queues that the executor has. Each task queue holds a queue of tasks. A queue manager decides which task queue to run. In our V1, the queue manager will simply pick an arbitrary task queue to run at any moment.
We will cover asynchronous I/O and io_uring in Phase 2.
Next, let's perform a deep dive into the implementation details.